
Uterus Cancer
Overview
Uterus cancer, also known as endometrial cancer, primarily affects the lining of the uterus (endometrium). It is the most common type of cancer of the female reproductive organs.
Types of Uterus Cancer
• Endometrial Carcinoma: The most common type, originating in the endometrial lining.
• Uterine Sarcoma: A rarer type that starts in the muscles or other tissues in the uterus.
Risk Factors
• Age: Most common in women over 50.
• Hormone Replacement Therapy: Especially estrogen-only therapy.
• Obesity: Excess fat can alter hormone balance.
• Menstrual History: Early menstruation or late menopause increases risk.
• Reproductive History: Never being pregnant.
• Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS): Can cause hormonal imbalances.
• Genetics: Family history of uterine or colorectal cancer.
• Diet and Exercise: Poor diet and lack of physical activity.
• Tamoxifen: Use of this breast cancer drug.
Symptoms
• Abnormal vaginal bleeding or discharge.
• Pelvic pain.
• Pain during intercourse.
• Weight loss.
• Pain during urination.
Diagnosis
• Pelvic Examination: Initial physical exam.
• Ultrasound: Imaging to view the uterus.
• Endometrial Biopsy: Removing a sample of the endometrial tissue for testing.
• Hysteroscopy: Visual examination of the uterine lining.
• Dilation and Curettage (D&C): A procedure to scrape and collect tissue from inside the uterus.
Treatment
• Surgery:
i. Hysterectomy: Removal of the uterus.
ii. Bilateral Salpingo-Oophorectomy: Removal of the fallopian tubes and ovaries.
• Radiation Therapy: High-energy rays to kill cancer cells.
• Hormone Therapy: For cancers that are hormone receptor-positive.
• Chemotherapy: Use of drugs to kill cancer cells.
• Targeted Therapy: Drugs that target specific cancer cell mechanisms.
Prognosis
The prognosis depends on factors such as the stage of cancer at diagnosis, the type of uterus cancer, patient age, and overall health. Early detection typically results in a better prognosis.
Prevention
• Maintaining a healthy weight.
• Regular exercise.
• Balanced diet.
• Monitoring and managing health conditions like PCOS and diabetes.
• Regular screenings and check-ups if you have risk factors.
If you experience symptoms or have risk factors associated with uterus cancer, it’s crucial to seek medical advice for appropriate screening and early intervention.
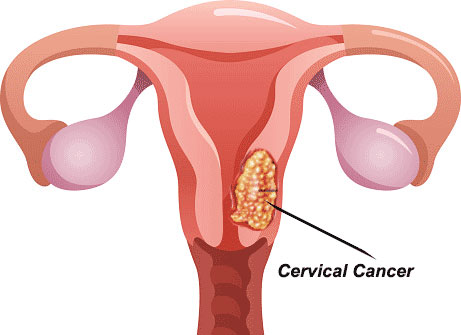
Uterine Cervix Cancer (Cervical Cancer)
Overview
Cervical cancer occurs in the cells of the cervix, the lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina. Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection is the primary cause of most cervical cancers.
Risk Factors
• HPV Infection: Most significant risk factor.
• Smoking: Increases the risk of cervical cancer.
• Immunosuppression: Weakened immune system, such as in HIV infection.
• Multiple Sexual Partners: Increases the risk of HPV infection.
• Early Sexual Activity: Exposure to HPV at an early age.
Symptoms
• Abnormal vaginal bleeding (after intercourse, between periods, or after menopause).
• Unusual vaginal discharge.
• Pelvic pain or pain during intercourse.
Diagnosis
• Pap Smear (Pap Test): Screening test to detect precancerous or cancerous cells on the cervix.
• HPV DNA Test: Detects the presence of high-risk HPV types.
• Colposcopy: Detailed examination of the cervix using a magnifying instrument.
• Biopsy: Sampling of cervical tissue for laboratory analysis.
Treatment
• Surgery: Options include conization, hysterectomy, and radical hysterectomy depending on the stage.
• Radiation Therapy: Often combined with chemotherapy for advanced stages.
• Chemotherapy: Used for advanced cancer or in combination with radiation.
• Targeted Therapy: Drugs that target specific cancer cell mechanisms.
• Immunotherapy: Stimulates the immune system to attack cancer cells.
Prevention and Early Detection
• HPV Vaccination: Protects against the types of HPV that cause most cervical cancers.
• Regular Screening: Pap tests and HPV tests for early detection of cervical changes.
• Safe Sexual Practices: Using condoms and limiting the number of sexual partners to reduce the risk of HPV infection.
• Lifestyle Choices: Maintaining a healthy weight, balanced diet, and avoiding smoking.
Early detection and treatment are crucial in improving outcomes for both uterine and cervical cancers. Regular gynecological check-ups and awareness of symptoms can lead to early diagnosis and better treatment success rates.