
Stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer, originates in the stomach's lining. It's often diagnosed in later stages due to vague early symptoms like indigestion, stomach pain, nausea, and loss of appetite. Risk factors include Helicobacter pylori infection, smoking, certain dietary habits (such as high salt and smoked foods), and genetic predisposition. Diagnosis typically involves endoscopy, imaging tests, and biopsy. Treatment options depend on the stage and may include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation, and targeted therapies. Early detection is crucial for better outcomes.
Small bowel cancer, or small intestine cancer, is a rare type of cancer that occurs in the small intestine, the part of the gastrointestinal tract that connects the stomach to the large intestine. Symptoms can include abdominal pain, weight loss, nausea, and blood in the stool. Risk factors include Crohn's disease, celiac disease, genetic conditions like Lynch syndrome, and a diet high in red and processed meats. Diagnosis typically involves imaging tests, endoscopy, and biopsy. Treatment options often include surgery, chemotherapy, and targeted therapies. Early detection is essential for improving survival rates.
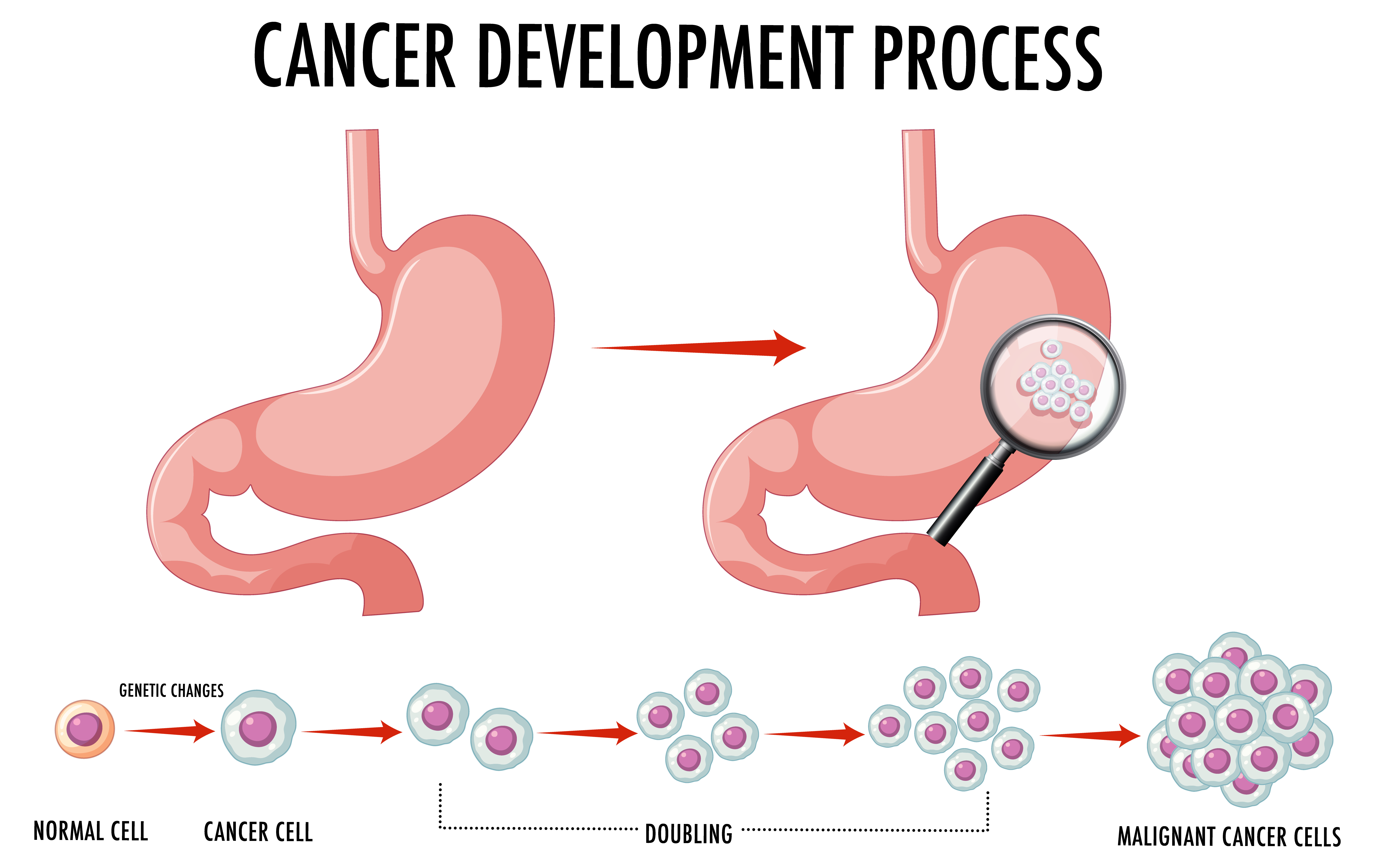
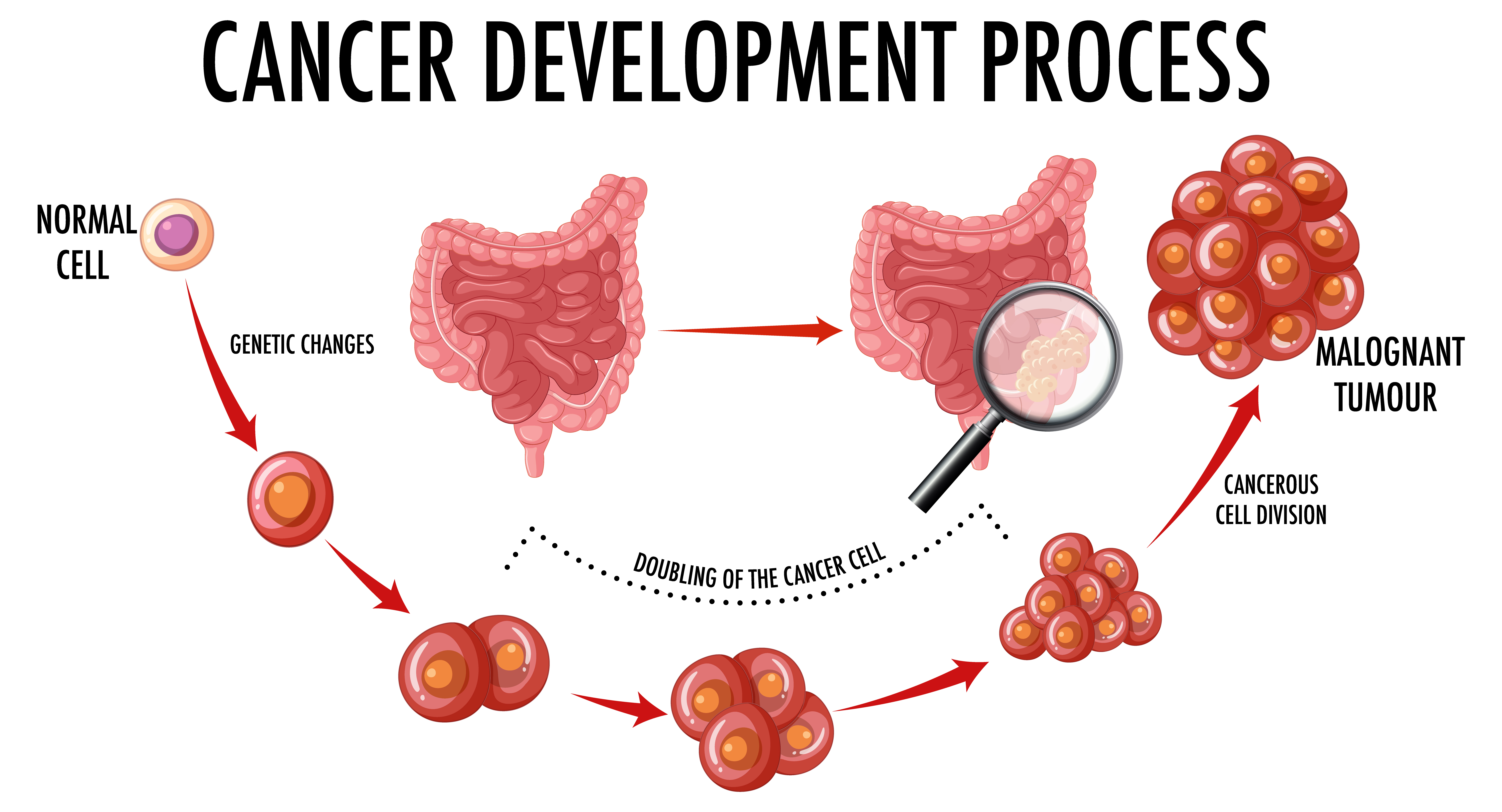
Colon cancer, also known as colorectal cancer when it involves the rectum, originates in the large intestine (colon). Symptoms can include changes in bowel habits, blood in the stool, abdominal discomfort, and unexplained weight loss. Risk factors include age, family history, a diet high in red or processed meats, smoking, heavy alcohol use, and conditions like inflammatory bowel disease. Screening methods like colonoscopy are crucial for early detection. Treatment typically involves surgery, chemotherapy, radiation, and targeted therapies. Early detection and removal of precancerous polyps can significantly improve survival rates.
Rectal cancer develops in the rectum, the final segment of the large intestine leading to the anus. Symptoms may include rectal bleeding, changes in bowel habits, a feeling of incomplete bowel evacuation, and abdominal pain. Risk factors encompass age, family history, a diet high in red or processed meats, smoking, heavy alcohol use, and conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease. Diagnosis often involves digital rectal exams, colonoscopy, and imaging tests. Treatment options include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and targeted therapies. Early detection through screening significantly improves treatment outcomes and survival rates.