Treatment
• Surgical Removal: The most common treatment, especially for BCC and SCC.
• Mohs Surgery: A precise surgical technique used to treat skin cancer. Layers of cancer-containing skin are progressively removed and examined until only cancer-free tissue remains.
• Radiation Therapy: Used for cancers that cannot be surgically removed.
• Chemotherapy: Typically for more advanced skin cancers.
• Immunotherapy and Targeted Therapy: Often used for melanoma.
Prevention
• Sun Protection: Using sunscreen, wearing protective clothing, and avoiding peak sun hours.
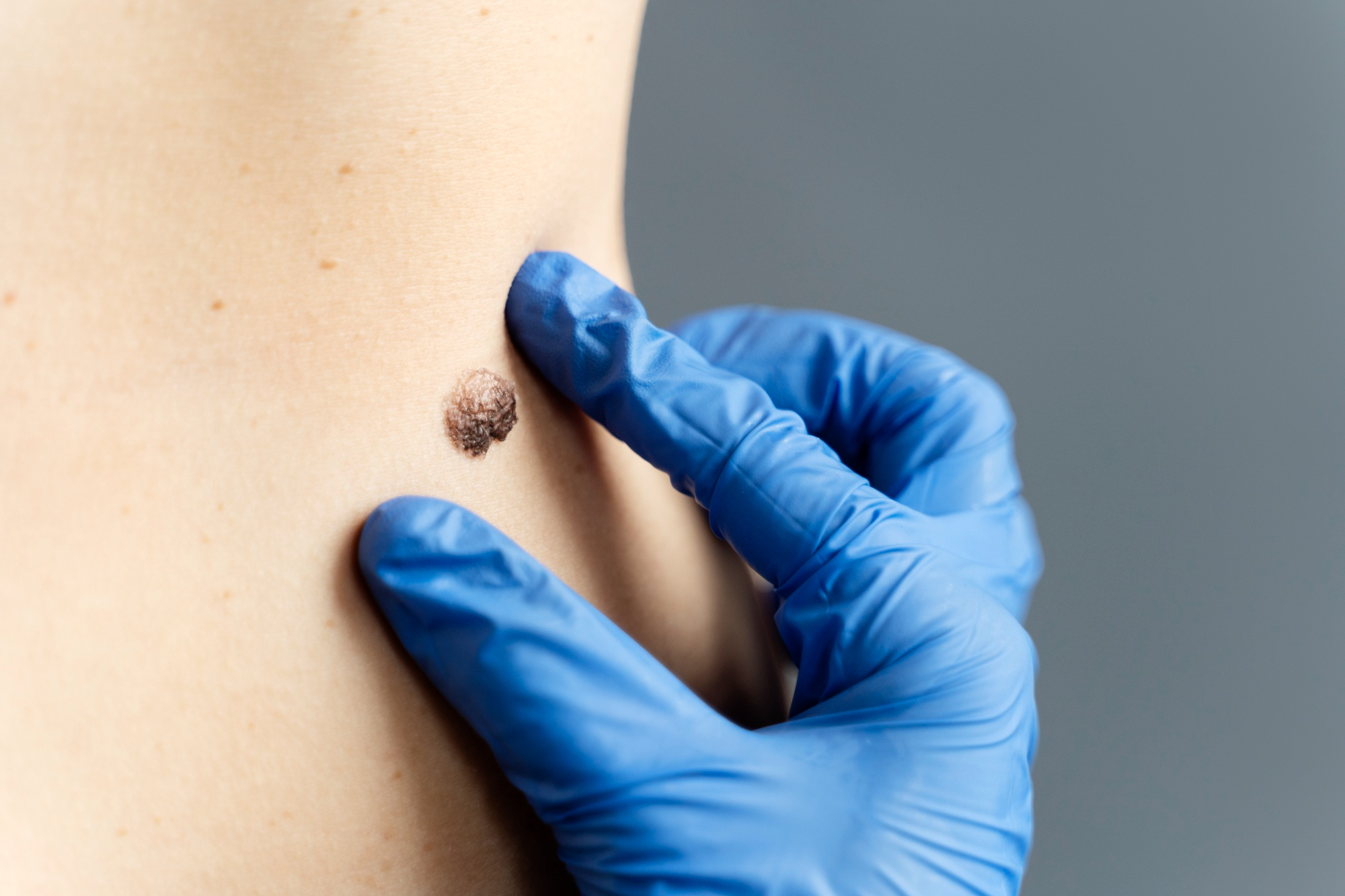
• Regular Skin Checks: Both self-examinations and professional skin exams.
• Avoiding Tanning Beds: They increase the risk of all skin cancers.
Prognosis
• Basal Cell Carcinoma and Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Generally have a high cure rate if detected early.
• Melanoma: The prognosis depends on the stage at diagnosis. Early-stage melanomas can often be cured, but advanced melanoma can be more challenging to treat.
Skin cancer is largely preventable and highly treatable when detected early. Awareness of risk factors, symptoms, and preventive measures is crucial for reducing the incidence and improving outcomes. Regular skin examinations and protection from UV radiation are key strategies in combating skin cancer.