
Thoracic cancer refers to a group of cancers that occur in the thoracic cavity, which is the part of the body located between the neck and the abdomen. This category primarily includes cancers of the lungs, esophagus, and thymus. Here's an overview of the main types of thoracic cancer:
1. Lung Cancer
Types:
• Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): The most common type, accounting for about 85% of cases. Subtypes include adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and large cell carcinoma.
• Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC): A more aggressive form, making up about 10-15% of lung cancers.
Risk Factors:
• Smoking (the leading cause)
• Exposure to radon gas
• Occupational exposure to carcinogens (e.g., asbestos, diesel exhaust)
• Family history of lung cancer
• Air pollution
Symptoms:
• Persistent cough
• Chest pain
• Shortness of breath
• Unexplained weight loss
• Fatigue
• Coughing up blood
Diagnosis:
• Imaging tests (CT scan, PET scan, X-rays)
• Biopsy
• Bronchoscopy
• Molecular testing
Treatment:
• Surgery
• Radiation therapy
• Chemotherapy
• Targeted therapy
• Immunotherapy
2. Esophageal Cancer
Types:
• Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Typically occurs in the upper and middle parts of the esophagus.
• Adenocarcinoma: Usually occurs in the lower part of the esophagus and is associated with Barrett’s esophagus.
Risk Factors:
• Smoking
• Heavy alcohol consumption
• Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
• Barrett’s esophagus
• Obesity
• Diets low in fruits and vegetables
Symptoms:
• Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
• Unintended weight loss
• Chest pain or discomfort
• Persistent cough or hoarseness
• Heartburn
Diagnosis:
• Endoscopy
• Biopsy
• Imaging tests (CT, PET scans)
• Barium swallow (esophagram)
Treatment:
• Surgery
• Radiation therapy
• Chemotherapy
• Targeted therapy
• Endoscopic treatments (e.g., stent placement, ablation)
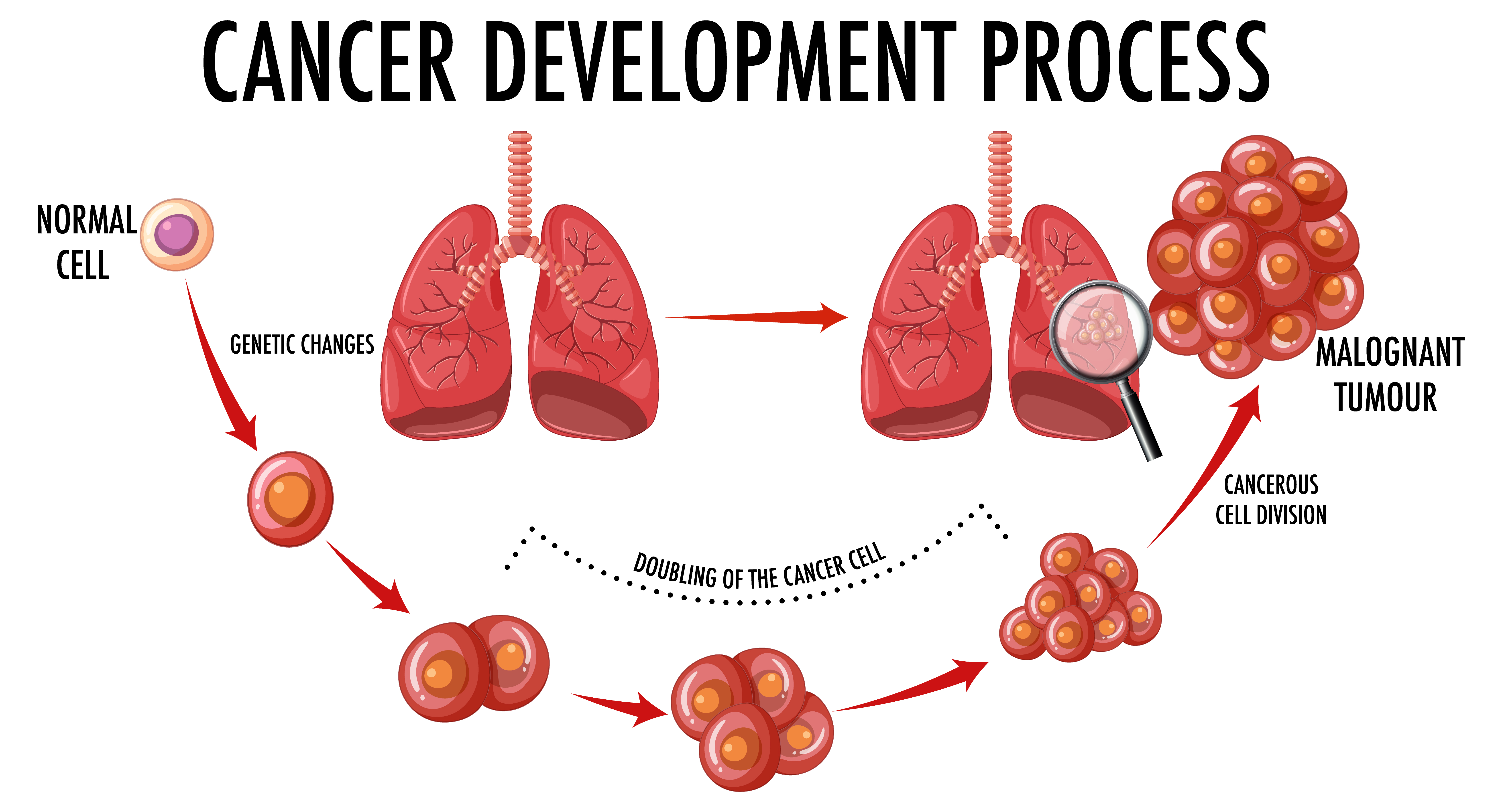
3. Thymic Cancer
Types:
• Thymoma: Generally slow-growing and often encapsulated.
• Thymic Carcinoma: More aggressive and can spread to other parts of the body.
Risk Factors:
• Myasthenia gravis
• Autoimmune diseases (e.g., lupus, rheumatoid arthritis)
• Family history (less commonly understood)
Symptoms:
• Persistent cough
• Chest pain
• Shortness of breath
• Muscle weakness
• Difficulty swallowing
Diagnosis:
• Imaging tests (CT scan, MRI)
• Biopsy
• Blood tests to check for associated autoimmune diseases
Treatment:
• Surgery
• Radiation therapy
• Chemotherapy
• Targeted therapy
General Points on Thoracic Cancer
Prevention:
• Avoid smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke
• Reduce alcohol consumption
• Maintain a healthy diet rich in fruits and vegetables
• Regular screening and monitoring for those at high risk (e.g., history of GERD, smoking)
Prognosis:
The prognosis varies widely depending on the type of cancer, stage at diagnosis, and overall health of the patient. Early detection and advances in treatment options have improved outcomes for many types of thoracic cancer.
If you have any specific questions or need detailed information about a particular aspect of throat cancer, feel free to ask!