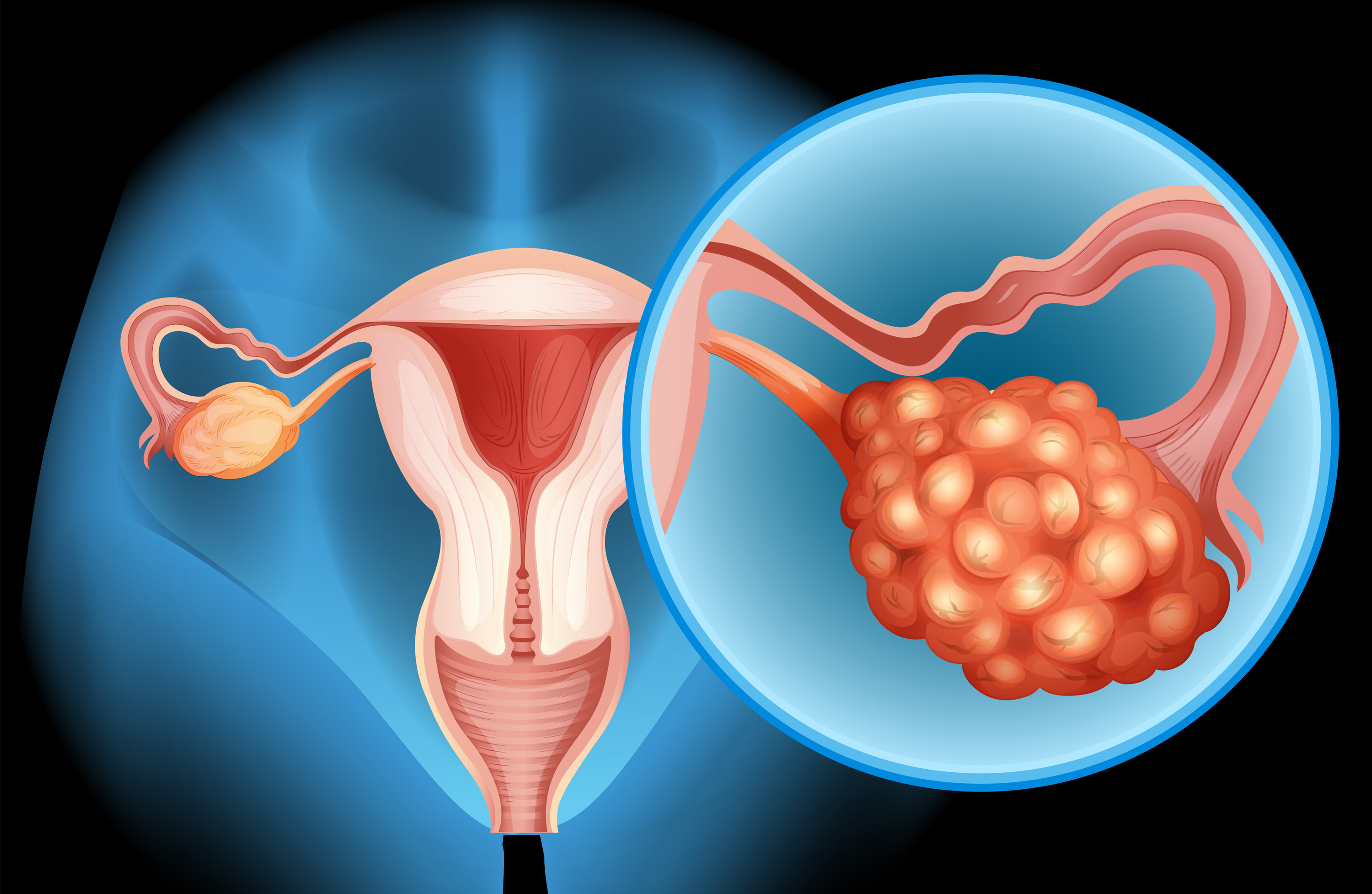
Ovary Cancer
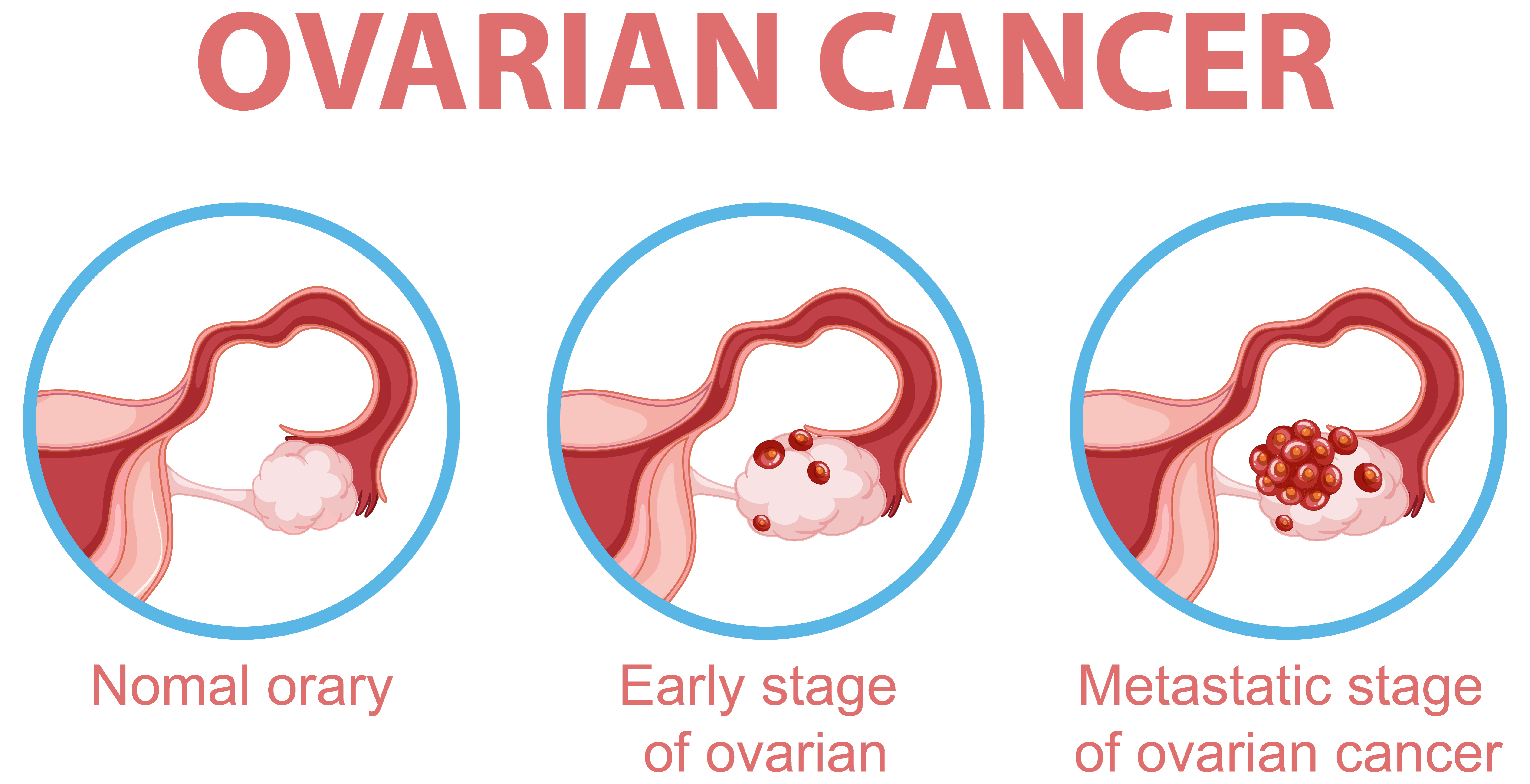
Ovarian cancer is a type of cancer that begins in the ovaries, which are the female reproductive glands where eggs are produced. It is known for being difficult to detect in its early stages and is often diagnosed at a later stage when it has already spread to other parts of the pelvis and abdomen.
Overview
Types of Ovarian Cancer:
• Epithelial Tumors: Most common type, arising from the cells on the surface of the ovary.
• Germ Cell Tumors: Rare, arising from the cells that produce eggs.
• Stromal Tumors: Also rare, arising from the structural tissue cells that hold the ovary together and produce female hormones.
Symptoms:
• Bloating or swelling of the abdomen
• Quickly feeling full when eating
• Weight loss
• Discomfort in the pelvis area
• Changes in bowel habits, such as constipation
• Frequent need to urinate
Risk Factors:
• Age (most common in women over 50)
• Family history of ovarian or breast cancer
• Genetic mutations (e.g., BRCA1 and BRCA2)
• Hormone replacement therapy
• Endometriosis
Diagnosis:
• Pelvic examination
• Imaging tests (ultrasound, CT scans)
• Blood tests (e.g., CA-125)
• Biopsy
HIPEC (Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy)
HIPEC is a treatment method that combines surgery and heated chemotherapy to treat cancers within the abdominal cavity, including advanced ovarian cancer.
Procedure:
• Cytoreductive Surgery: First, the surgeon removes as much of the visible tumor as possible from the abdominal cavity. This is known as debulking surgery.
• Hyperthermic Chemotherapy: After the tumor is removed, a heated chemotherapy solution is circulated throughout the abdominal cavity. The solution is usually heated to about 41-43°C (105.8-109.4°F). This process typically lasts for about 60-90 minutes.
Benefits:
• Directly targets cancer cells in the abdominal cavity, where ovarian cancer often spreads.
• Heat enhances the effectiveness of the chemotherapy, helping to kill more cancer cells.
• Reduces systemic side effects compared to traditional intravenous chemotherapy since the drugs are largely confined to the abdominal cavity.
Considerations:
• HIPEC is generally used for advanced-stage cancer.
• Not all patients are candidates; suitability depends on factors such as overall health, extent of cancer spread, and response to previous treatments.
• Potential side effects include infection, bleeding, kidney dysfunction, and bowel complications.
Outcomes:
• Studies have shown improved survival rates and reduced recurrence in some patients with advanced ovarian cancer treated with HIPEC.
• Ongoing research is assessing the long-term benefits and potential risks.
Ovarian cancer remains a challenging disease to treat, particularly when diagnosed at an advanced stage. HIPEC offers a promising treatment option for some patients by combining surgical removal of tumors with targeted, heated chemotherapy. As with all treatments, it is important for patients to discuss the potential benefits and risks with their healthcare team to determine the best course of action based on their individual circumstances.